dna damage response replication arrest
The DDR protects genome stability through the precise coordination of a network of pathways. Targeting Hypoxic Cells through the DNA Damage Response Exposure to hypoxia.
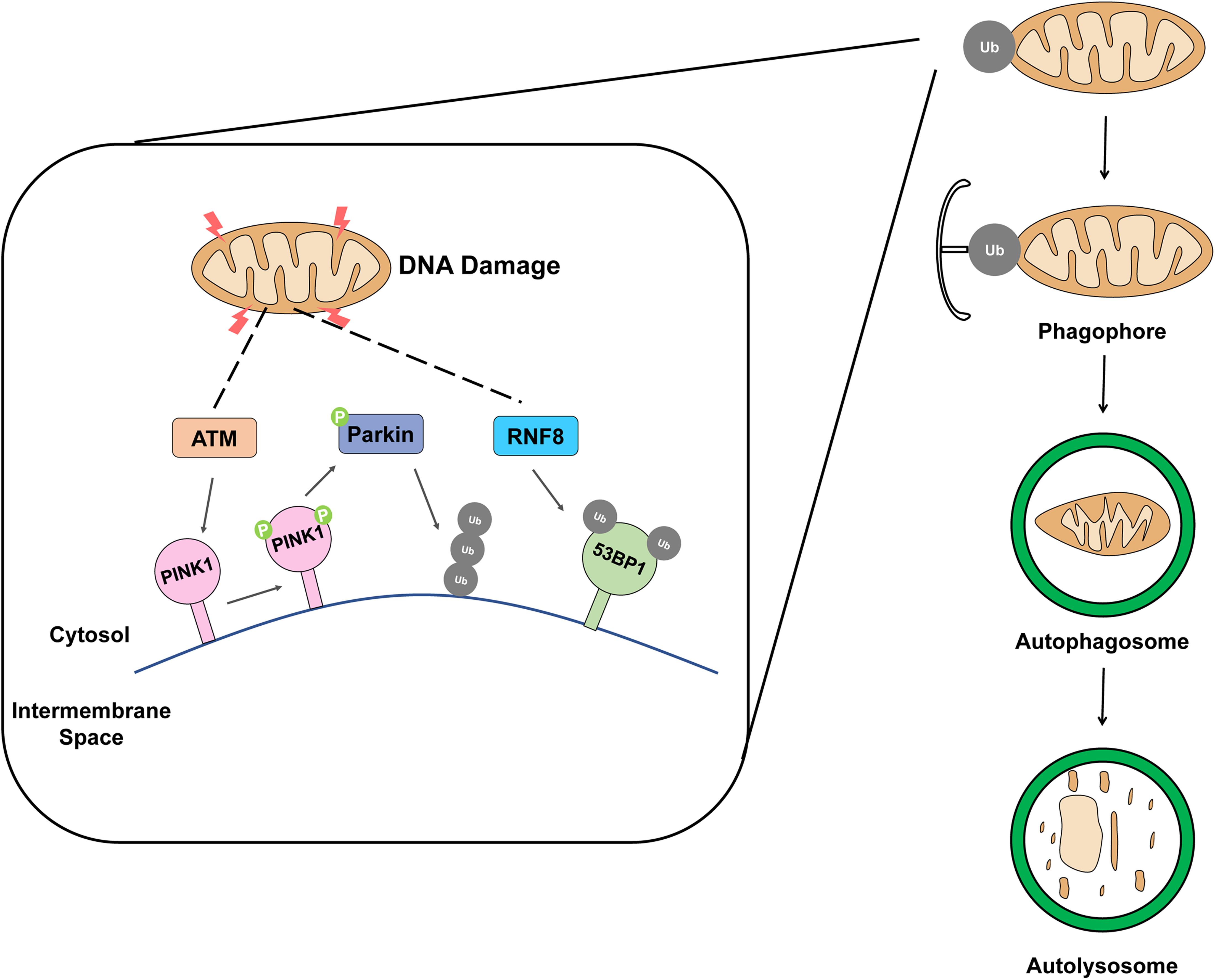
Frontiers Autophagic Organelles In Dna Damage Response Cell And Developmental Biology
Human parvovirus B19 DNA replication induces a DNA damage response that is dispensable for cell cycle arrest at phase G2M.

. Here we describe an additional mechanism that prevents DNA replication in response to DNA damage. Since both viral simian virus 40 SV40 and cellular DNA replication are inhibited at similar CPI levels it is possible to use the more easily studied viral system to elucidate how CPI treatment results in DNA replication arrest. The most likely explanation for this trans-inhibition of DNA replication is through cellular DNA damage response pathways or checkpoints.
2 Upon sensing DNA damage or stalls in replication cell cycle checkpoints are activated to arrest cell cycle progression to allow time for repair before the damage is passed on to daughter cells. Activation of the pathway produces a diffusible inhibitor of DNA replication which ultimately blocks chromosomal replication by preventing the essential replication factor PCNA from loading. Mutations in LMNA result in altered nuclear morphology but how this impacts the mechanisms that maintain genomic stability is unclear.
Lamin AC depletion enhances DNA damage-induced stalled replication fork arrest. The DNA damage response DDR comprises a set of signaling pathways for the detection and repair of DNA damage and includes the MMR system for mispaired bases the base excision repair system for small base modifications the nucleotide excision repair for intrastrand crosslinks and pyrimidine dimers the single-strand break repair and double-strand break DSB. Exposure to hypoxia-induced replication arrest initiates a DNA damage response that includes both ATR- and ATM-mediated signaling.
In this situation MK2 activity determines the decision between replication fork stalling and. This inhibitory activity is not due to sequestration of replication factors. Very frequent replicating cells.
The arrest of chromosomal segregation in response to misalignment of the mitotic spindle. Failure to reactivate stalled or collapsed DNA replication forks is a potential source of genomic instability. DNA fiber analysis was used to show that these conditions lead to a replication arrest during both the initiation and elongation phases and that this correlated with decreased levels of nucleotides.
MMS is known to inhibit replication though activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and through checkpoint-independent slowing. DNA molecules are subject to various lesions that can be detrimental to the cells. Thaliana atm mutant shows hypersensitivity to gamma irradiation and the DNA-alkylating agent methyl methanesulfonate and defects in meiosis Garcia et al 2003.
Since replication checkpoints have also been associated with suppression of recombination in S phase and mutation suppression see the above section and the 9-1-1 checkpoint complex in fission yeast was suggested to promote mutagenesis in response to replication stress it would be of great interest to determine whether there is coordination. Download scientific diagram Hypoxia-induced replication arrest triggers a DNA damage response from publication. Generally DNA double-strand breaks DSBs activate ATM whereas ATR is activated in response to single stranded DNA which is generated as a repair intermediate or by replication arrest.
Structural changes to DNA severely affect its functions such as replication and transcription and play a major role in age-related diseases and cancer. When DNA lesions occur during the S phase of the cell cycle replication fork progression is blocked because it can be responsible for the replication-associated DNA DSBs which are. This pathway is activated by alkylation damage of DNA.
DNA breaks and activation of the DNA damage response DDR arising from endogenous replication stress have been observed at early or precancerous stages and adaptation to replication stress plays an important role in tumour development 17181920. We have recently reported another mechanism by which DNA damage affects replication in which the presence of damaged DNA inhibits in trans the initiation of chromosomal replication. Based on the central role of DNA damage for ageing we propose a tentative model Figure 7 in which different DNA repair and damage response systems linked with replication and transcription cell cycle arrest senescence cell death and mutagenesis are differentially employed as anti-ageingcancer strategies.
A complicated and entangled network of DNA damage response DDR mechanisms including multiple DNA repair pathways damage tolerance processes and cell-cycle checkpoints safeguard genomic integrity. If a high level of DNA damage occurs cell-cycle checkpoint proteins become activated and arrest the cell-cycle thus preventing the transmission of damaged DNA during mitosis. The arrest of the cell cycle in response to damaged and unreplicated DNA to ensure proper completion of S phase.
Both single-stranded DNA generated by replication fork arrest and DNA strand break formation resulting from DNA dam-age or from replication fork collapse activate downstream DDR pathways mediated by the phosphoinositide-3-kinase PI-3K-related protein kinases PIK kinases including ataxiav telangi-. This inhibition occurs by blocking the association of the processivity clamp PCNA with undamaged chromatin. Chromosomal replication is sensitive to the presence of DNA-damaging alkylating agents such as methyl methanesulfonate MMS.
The arrest of the cell cycle in response to DNA damage to prevent its replication. All eukaryotic cells have evolved a multifaceted response to counteract the potentially deleterious effects of DNA damage Figure1. The DNA damage response DDR comprises a set of signaling pathways for the detection and repair of DNA damage and includes the MMR system for mispaired bases the base excision repair system for small base modifications the nucleotide excision repair for intra-strand crosslinks and pyrimidine dimers and the single-strand break repair and double-strand break.
Homologous recombination HR is a major mechanism for repairing the DNA damage resulting from replication arrest. The regulation of epigenetic modifications. Our results imply a direct impact of the p38MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2 MK2 kinase pathway on the cellular response to replicative stress.
The human LMNA gene encodes the essential nuclear envelope proteins lamin A and C lamin AC. The single-strand DNA ssDNA-binding protein replication protein A RPA plays a major role in multiple processes of DNA metabolism. Request PDF A Novel Replication Arrest Pathway in Response to DNA Damage DNA damage has been shown to regulate DNA replication both by.
Human parvovirus B19 B19V infection is highly restricted to human erythroid progenitor cells in which it induces a DNA damage response DDR. DNA damage response DDR pathways encompass a variety of mechanisms that cells employ in response to.

Stalled Dna Replication Fork Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Damage Response An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dna Replication Checkpoint Dna Synthesis Learn Science At Scitable
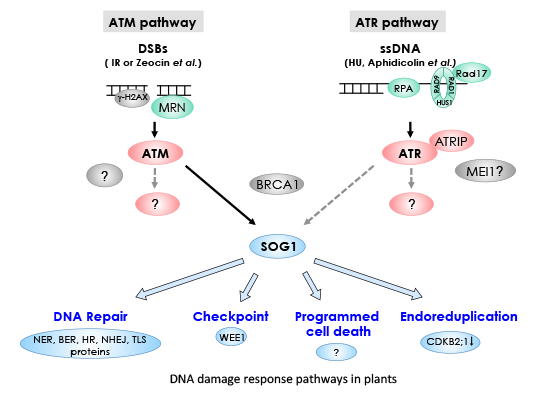
Biology Free Full Text Dna Damage Response In Plants Conserved And Variable Response Compared To Animals Html
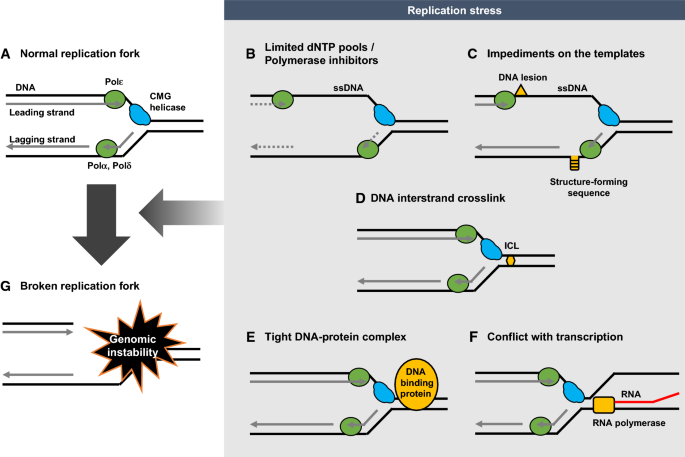
Dna Damage Responses That Enhance Resilience To Replication Stress Springerlink
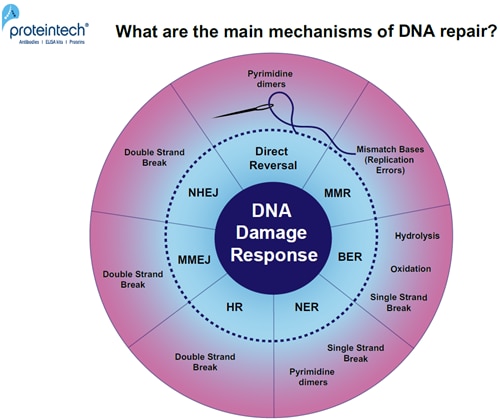
How To Solve The Genome Dna Damage Proteintech Group

Exploiting Replicative Stress In Gynecological Cancers As A Therapeutic Strategy International Journal Of Gynecologic Cancer
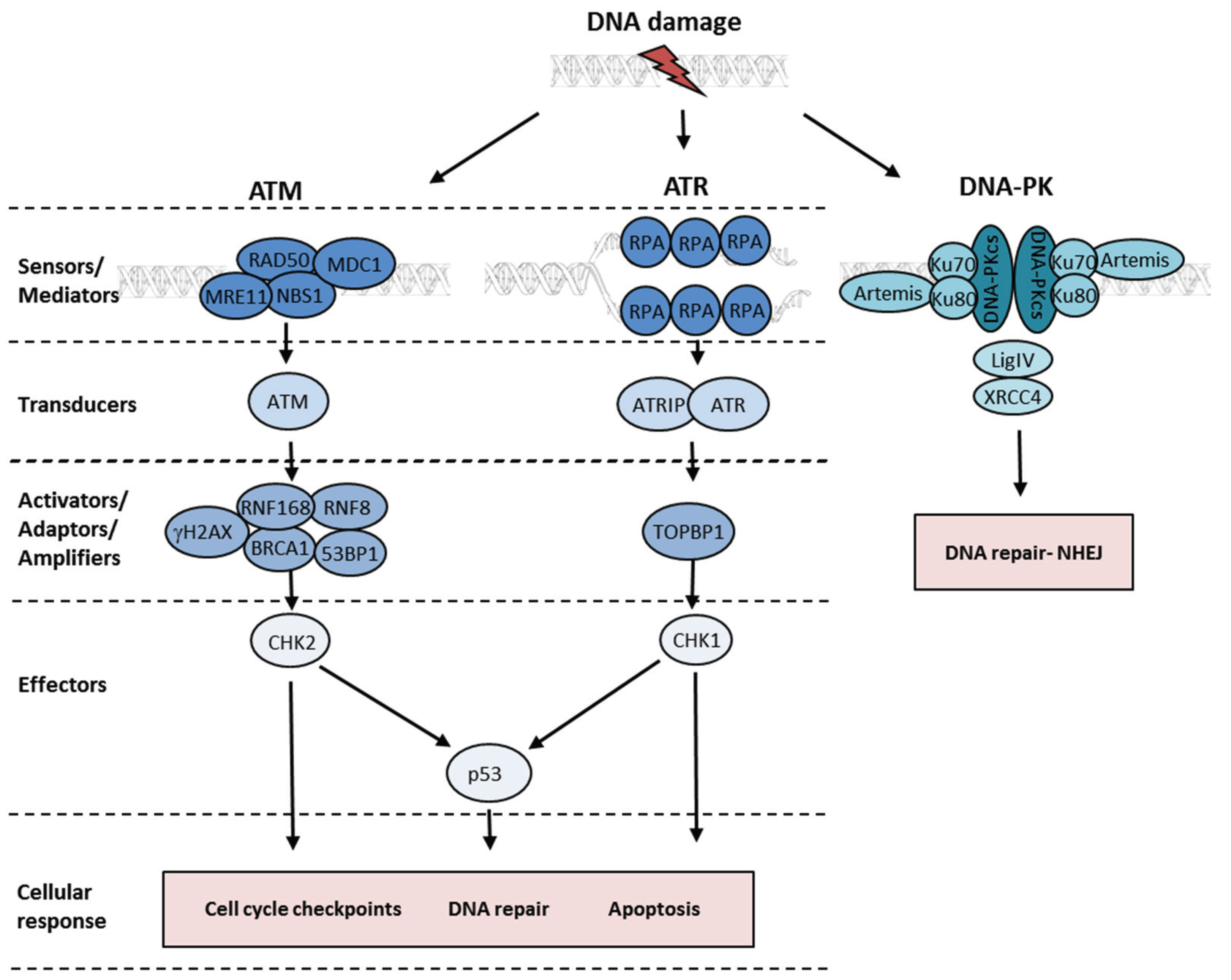
Biomolecules Free Full Text Activation Of The Dna Damage Response By Rna Viruses Html

Integration Of Dna Damage Responses With Dynamic Spatial Genome Organization Trends In Genetics

Targeting The Replication Stress Response Through Synthetic Lethal Strategies In Cancer Medicine Trends In Cancer
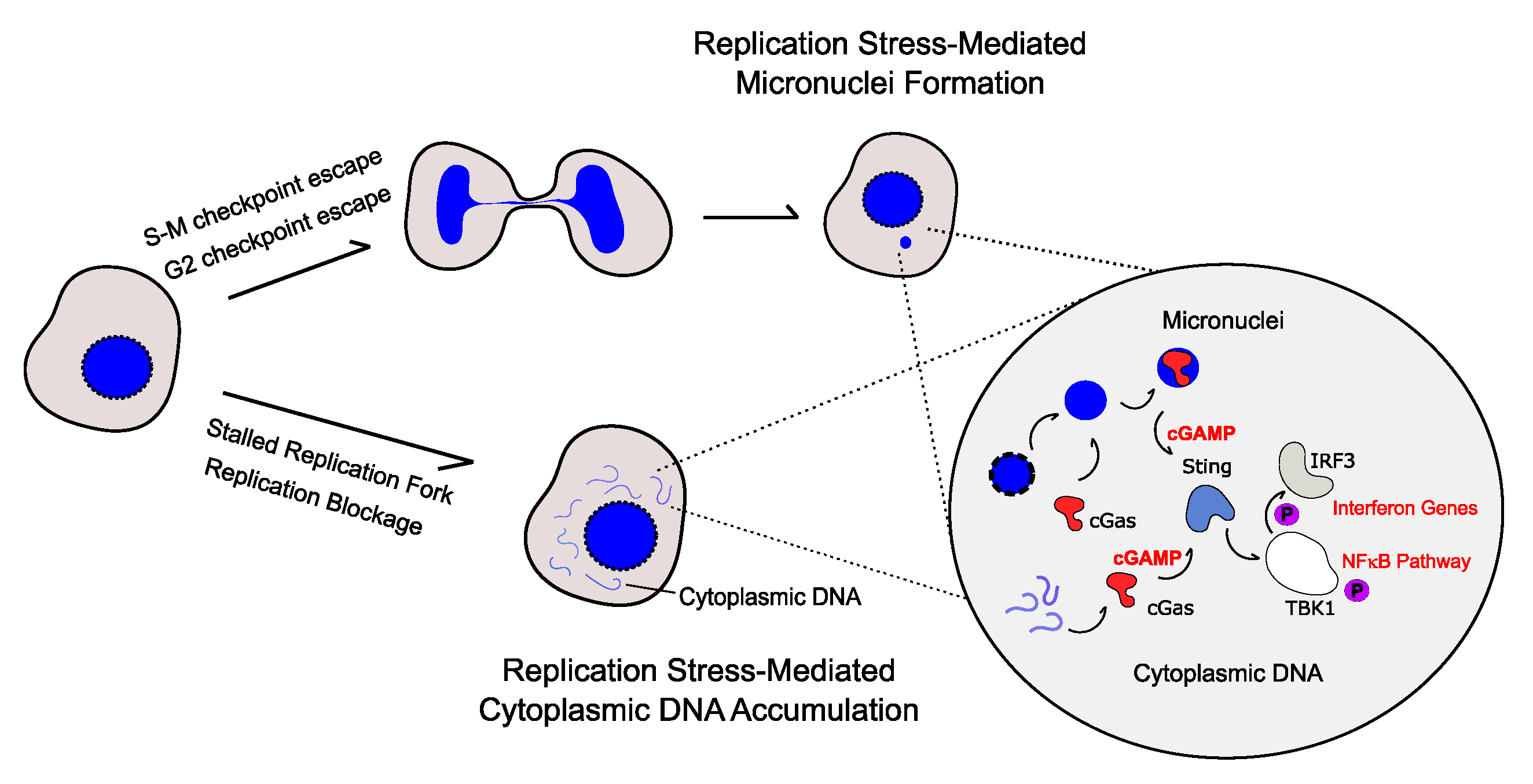
Genes Free Full Text Replication Stress Dna Damage Inflammatory Cytokines And Innate Immune Response Html

Quiz On Dna Replication Molecular Biology Dna Replication Biology
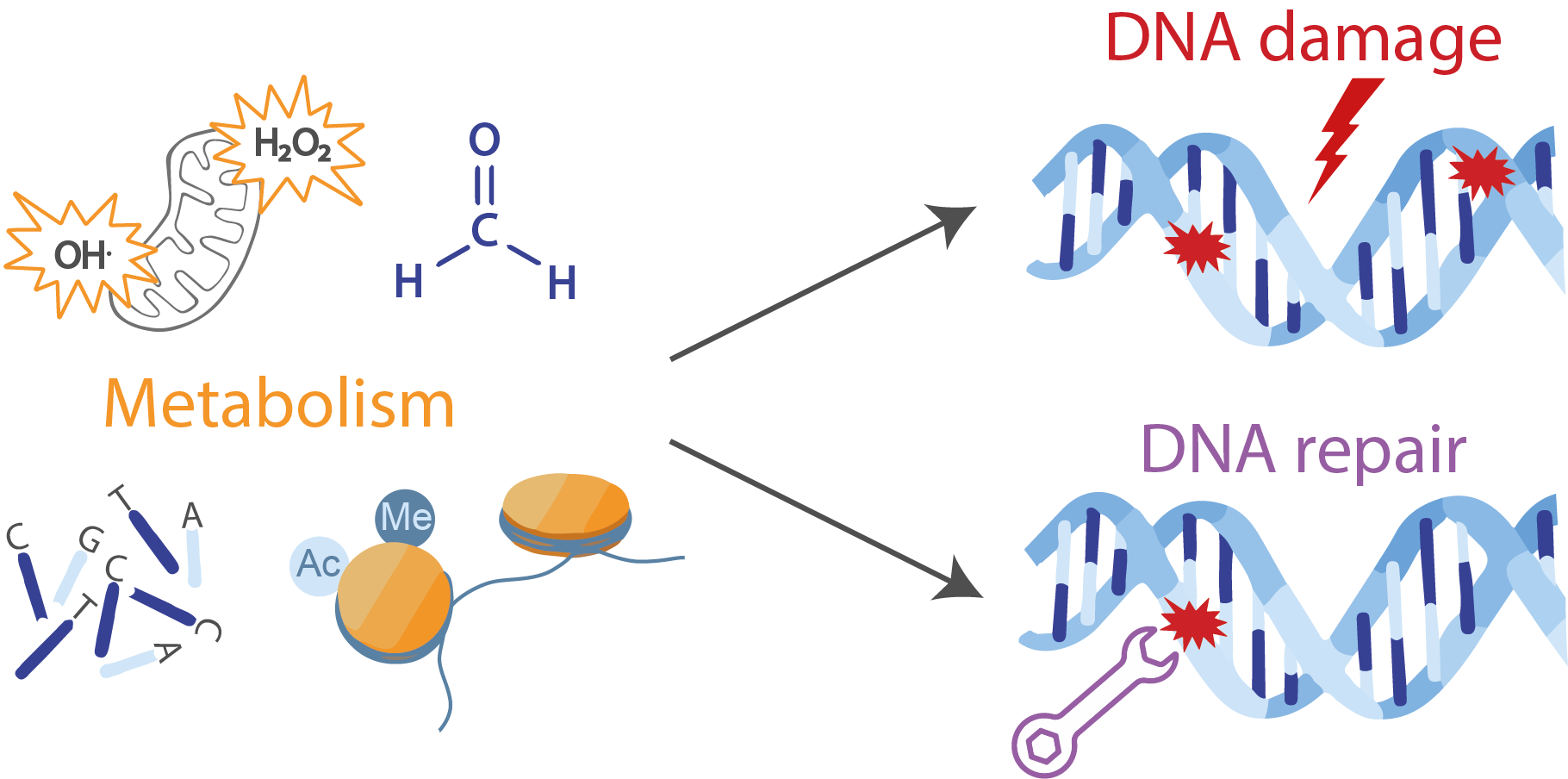
Cancers Free Full Text Interplay Between Cellular Metabolism And The Dna Damage Response In Cancer Html

Dna Replication Checkpoint Dna Synthesis Learn Science At Scitable
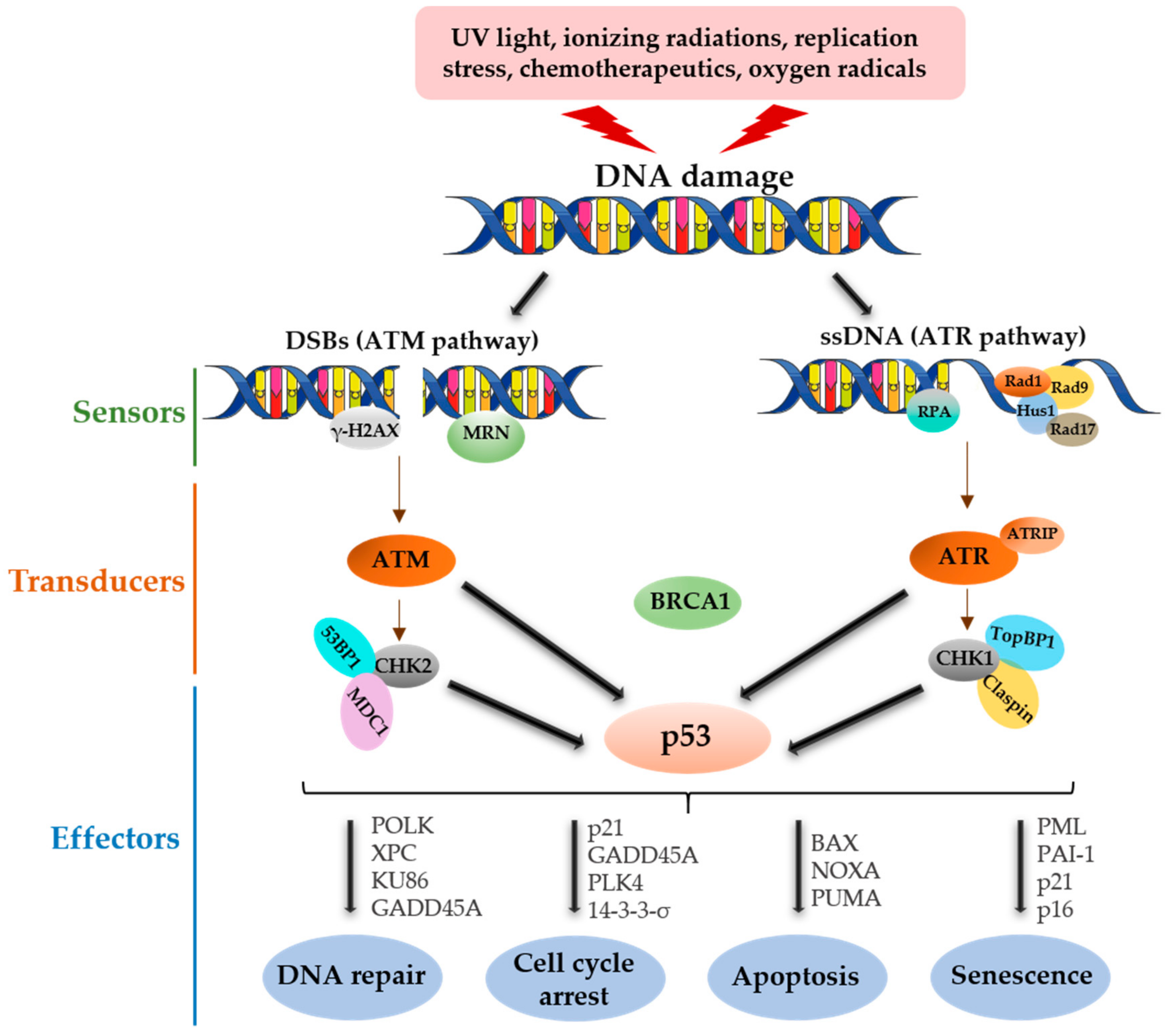
Genes Free Full Text P53 Mrna Metabolism Links With The Dna Damage Response Html




Comments
Post a Comment